Display Days until expiration date in Excel
This tutorial show how to Display Days until expiration date in Excel using the example below.
To calculate the days until an expiration date, you can use a simple formula based on the TODAY function.
Formula
=A1-TODAY()
Explanation of how this formula works
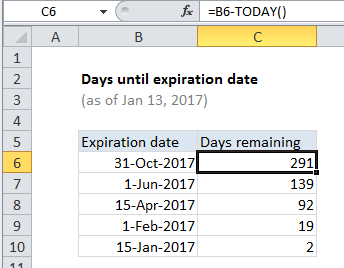
In the example shown, the formula in C6 is:
=B6-TODAY()
Dates in Excel are simply serial numbers. In the standard date system for Excel, January 1, 1900 is the number 1. January 1, 2017 is 42736, January 1, 2018 is 43101, and January 1, 2050 is the serial number 54,789.
As a result, you can use simple addition and subtraction to calculate dates. In this case, we have a date in the future, so need to subtract the current date to get “days remaining”. The TODAY function returns the current date automatically, so we only need to subtract the result of TODAY() from the date values in column B.
Note: if a date has passed, the result will be negative.
Creating an expiration date
To create an expiration date, given a date, you can simply add the number of days until expiration. With a date in A1:
=A1+30 // 30 days in the future =A1+90 // 90 days in the future