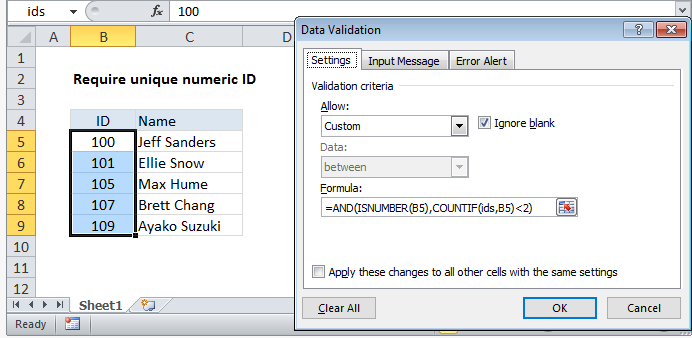
Excel Data validation require unique number
Set criteria to accept only unique number, ie no duplicate.
Formula
=AND(ISNUMBER(A1),COUNTIF(range,A1)<2)
Cell references in data validation formulas are relative to the upper left cell in the range selected when the validation rule is defined, in this case B5.
Explanation
In the example shown, the data validation applied to B5:B9 is:
=AND(ISNUMBER(B5),COUNTIF(ids,B5)<2)
where ids is the named range B5:B9.
How this formula works
Data validation rules are triggered when a user adds or changes a cell value.
The AND function takes multiple arguments (logical expressions) and returns TRUE only when all arguments return TRUE. In this case, we need two conditions:
Logical 1 tests if the input is a number using the ISNUMBER function:
ISNUMBER(B5)
The ISNUMBER function returns TRUE when a value is numeric and FALSE if not.
Logical 2 tests checks that the input doesn’t already exist in the named range “ids”:
COUNTIF(ids,B5)<2
COUNTIF returns a count of the value in B5 inside the named range ids (B5:B9). If the count is less than 2, the logical expression returns TRUE.
If both logical expressions return TRUE, the AND function returns TRUE and validation succeeds:
=AND(TRUE,TRUE) // validation successful
If either logical returns FALSE, data validation fails.
Note: Be aware that numeric input includes dates and times, whole numbers, and decimal values.