KURT function: Description, Usage, Syntax, Examples and Explanation
What is KURT function in Excel?
Syntax of KURT function
KURT(number1, [number2], …)
The KURT function syntax has the following arguments:
- Number1, number2, … Number1 is required, subsequent numbers are optional. 1 to 255 arguments for which you want to calculate kurtosis. You can also use a single array or a reference to an array instead of arguments separated by commas.
KURT formula explanation
- Arguments can either be numbers or names, arrays, or references that contain numbers.
- Logical values and text representations of numbers that you type directly into the list of arguments are counted.
- If an array or reference argument contains text, logical values, or empty cells, those values are ignored; however, cells with the value zero are included.
- Arguments that are error values or text that cannot be translated into numbers cause errors.
- If there are fewer than four data points, or if the standard deviation of the sample equals zero, KURT returns the #DIV/0! error value.
- Kurtosis is defined as:
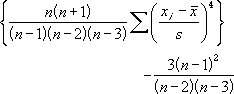 where s is the sample standard deviation.
where s is the sample standard deviation.
Example of KURT function
Steps to follow:
1. Open a new Excel worksheet.
2. Copy data in the following table below and paste it in cell A1
Note: For formulas to show results, select them, press F2 key on your keyboard and then press Enter.
You can adjust the column widths to see all the data, if need be.
| Data | ||
| 3 | ||
| 4 | ||
| 5 | ||
| 2 | ||
| 3 | ||
| 4 | ||
| 5 | ||
| 6 | ||
| 4 | ||
| 7 | ||
| Formula | Description | Result |
| =KURT(A2:A11) | Kurtosis of the data set above | -0.151799637 |