How to create running total in an Excel Table
This tutorial shows illustrates a Running total in Excel Table.
To create a running total in an Excel Table, you can use the INDEX function set up with a structured reference.
Formula
=SUM(INDEX([column],1):[@column])
Explanation
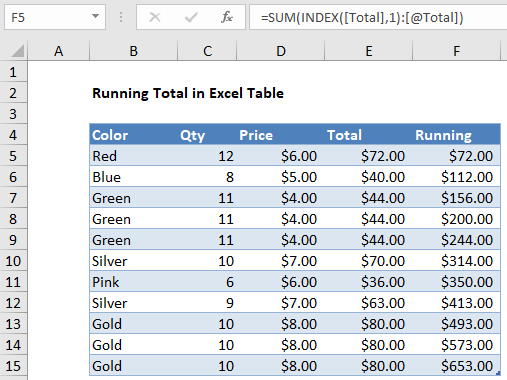
In the example shown, the formula in F5 is:
=SUM(INDEX([Total],1):[@Total])
When copied down the column, this formula will return a running total at each row.
How this formula works
At the core, this formula has a simple pattern like this:
=SUM(first:current)
Where “first” is the first cell in the Total column, and “current” is a reference to a cell in the current row of the Total column.
To get the a reference to the first cell, we use INDEX like this:
INDEX([Total],1)
Here, the array is the entire “Total” column and row number is 1. This works because, the INDEX function returns a reference to the first cell, not the actual value.
To get a reference to the current row, we use:
[@Total]
This is the standard structured reference syntax for “this row”.
The SUM function sums the values in the range at each row, creating a running total.
As the formula is copied down the column, the reference to the first cell doesn’t change, but the referent to the current cell changes at each row. The result is a reference that expands.
Simple expanding range
Why not use a simple expanding range like this?
=SUM($E$5:E5)
For some reason, this kind of mixed reference becomes corrupted in an Excel Table as rows are added. Using INDEX with a structured reference solves the problem.