How to randomly assign data to groups in Excel
To randomly people (or anything) to groups you can use the RANDBETWEEN function with the CHOOSE function.
Formula
=CHOOSE(RANDBETWEEN(1,3),"Group A","Group B","Group B")
Explanation
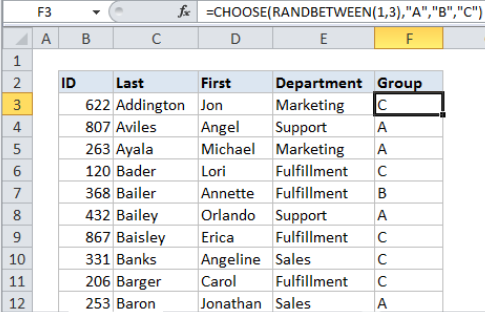
In the example shown, the formula in F3 is:
=CHOOSE(RANDBETWEEN(1,3),"A","B","C")
When copied down the column, this formula will generate a random group (A, B, or C) for each person in the list.
How this formula works
The RANDBETWEEN function generates random numbers between two integers. The CHOOSE function takes a number as the first argument, and uses that number to select the “nth” item from the following arguments.
So, in this formula, RANDBETWEEN generates a number between 1 and 3, this number is used to choose a group from the 3 following values: “A”,”B”,”C”.
You can use this same approach any time you need make random assignments. It’s especially useful when you you need to assign data to a limited number of text values.
Automatic recalculation
Be aware that RANDBETWEEN will re-calculate whenever there is any change to a workbook, or even when a workbook is opened. Once you have a set of random assignments, you may want to copy and paste the formulas as values to prevent further changes.