How to calculate Net Present Value (NPV) in Excel
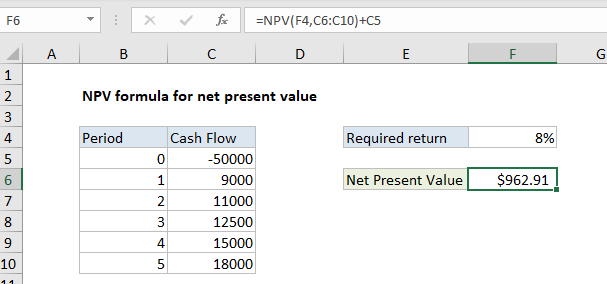
NPV formula for net present value
To calculate Net Present Value (NPV) you can use the NPV function.
Formula
=NPV(rate,cashflows)-initialcost
Explanation
In the example shown, the formula in F6 is:
=NPV(F4,C6:C10)+C5
How this formula works
Net Present Value (NPV) is the present value of expected future cash flows minus the initial cost of investment. The NPV function in Excel only calculates the present value of uneven cashflows, so the initial cost must be handled explicitly.
One way to calculate Net Present Value in Excel is to use NPV to get the present value of all expected cash flows, then subtract the initial investment. This is the approach taken in the example shown, where the formula in F6 is:
=NPV(F4,C6:C10)+C5
The NPV function returns 50962.91. The initial investment (-50,000, recorded as a negative value because it is an outflow) is then added, and the final result is 962.91.