Count cells that are not blank in Excel
This tutorial shows how to Count cells that are not blank in Excel using the example below;
Formula
=COUNTA(range)
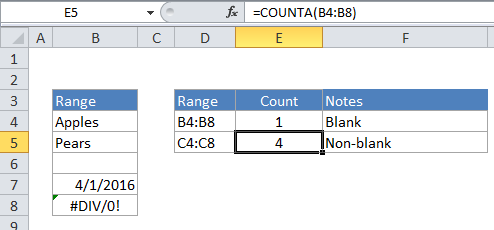
Explanation
To count the number of cells that are not blank in a range, you can use the COUNTA function. In the example shown, E5 contains this formula:
=COUNTA(B4:B8)
How this formula works
COUNTA is fully automatic. When given a range of cells, it counts cells that contain numbers, text, logical values, and errors. COUNTA does not count empty cells. To count cells that are blank, you can use the COUNTBLANK function like so:
=COUNTBLANK(B4:B8)
Count cells with at least one character
One problem with COUNTA is that it will also count empty strings returned by formulas (“”). If you run into this problem, you can try a formula like this:
=SUMPRODUCT(--(LEN(A1:A100)>0))
Here, the LEN function returns a character count for each cell in the range, which is then compared to zero with the greater than operator (>). This expression returns TRUE for cells that contain at least 1 character, and FALSE for others. The double-negative (–) is used to coerce the TRUE/FALSE values to ones and zeros, and the SUMPRODUCT function returns the sum.