VLOOKUP with numbers and text in Excel
This tutorial shows how to calculate VLOOKUP with numbers and text in Excel using the example below;
Formula
=VLOOKUP(val&"",table,col,0)
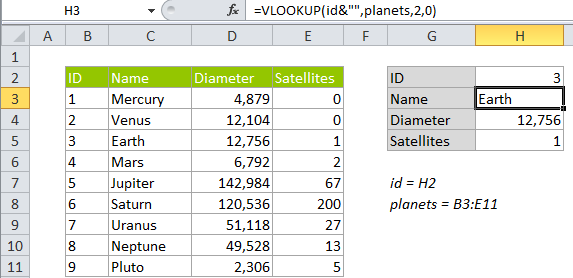
Explanation
A common problem with VLOOKUP is a mismatch between numbers and text. Either the first column in the table contains lookup values that are numbers stored as text, or the table contains numbers, but the lookup value itself is a number stored as text.
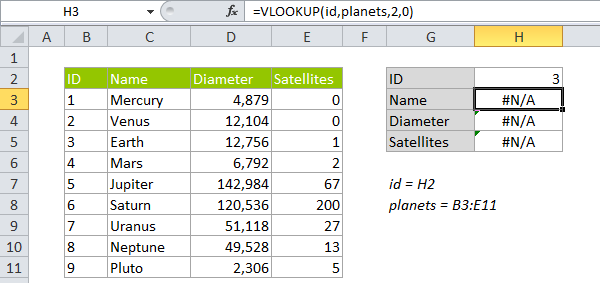
In either case, VLOOKUP will return an #N/A error, even when there appears to be a match. In the example below, each planet has an id based on position from the sun. In cell H3 we have a simple VLOOKUP formula looking for the number 3 from cell H2. The result is the #N/A error, even though 3 is clearly in the table.
One solution is to convert both the first column in the table and the lookup value to the same type: either numbers or text. However, if you don’t have control over both the table and the lookup value, or if it’s simply not practical to convert values, you can modify the VLOOKUP formula to coerce the lookup value to match the type in the table. In this case, we can revise the VLOOKUP formula to concatenate an empty string to the lookup value, which converts the lookup value to text:
=VLOOKUP(id,planets,2,0) // original =VLOOKUP(id&"",planets,2,0) // revised
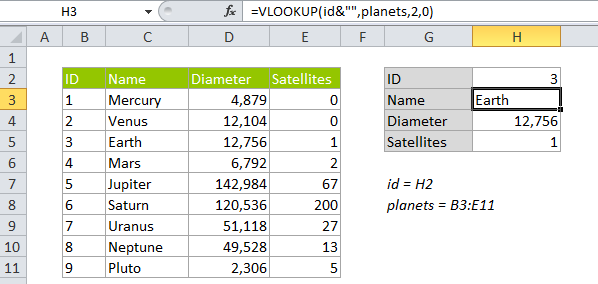
In the worksheet, the revised formula takes care of the error:
How this formula works
When you concatenate an empty string (“”) to a number, it converts the number to text. You could also do the same thing with a longer formula that utilizes the TEXT function to convert to text :
=VLOOKUP(TEXT(id,"@"),planets,2,0)
If you have both numbers and text
If you can’t be certain when you’ll have numbers and when you’ll have text, you can cater to both options by wrapping VLOOKUP in IFERROR and writing a formula that handles both cases:
=IFERROR(VLOOKUP(id,planets,3,0),VLOOKUP(id&"",planets,3,0))
Here, we first try a straight VLOOKUP formula that assumes both lookup value and the first column in the tables are numbers. If that throws and error, we try again with the revised formula. If that fails, VLOOKUP will return the #N/A error.