Highlight integers only in Excel
This tutorial shows how to Highlight integers only in Excel using the example below;
Formula
=MOD(A1,1)=0
Explanation
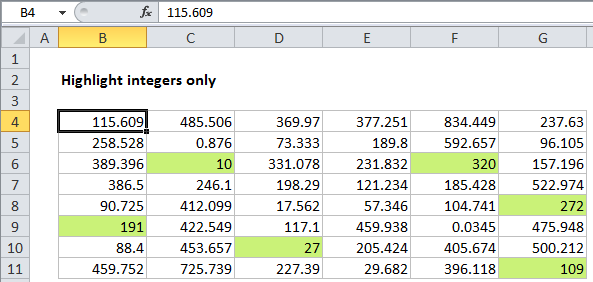
To highlight numbers that are integers, you can use a simple formula based on the MOD function. In the example shown, conditional formatting has been applied to the range B4:G11 using this formula:
=MOD(B4,1)=0
Note: it’s important that CF formulas be entered relative to the “active cell” in the selection, which is assumed to be B4 in this case.
Once you save the rule, you’ll see only values that are integers (whole numbers) highlighted.
How this formula works
The MOD function returns the remainder after division. With a divisor of 1, MOD will return zero for any whole number.
We use this fact to construct a simple formula that tests the result of MOD. When the result is zero (i.e. when the number is an integer) the formula returns TRUE, triggering the conditional formatting.
When the result is not zero (i.e. the number has a decimal component, and dividing by 1 leaves remainder) the formula returns FALSE.