How to strip protocol and trailing slash from URL in Excel
To remove the protocol (i.e. http://, ftp://, etc.) and trailing slash from a URL, you can use a formula based on the MID, FIND, and LEN functions.
Formula
=MID(url,FIND("//",url)+2,LEN(url)-FIND("//",url)-1-(RIGHT(url)="/"))
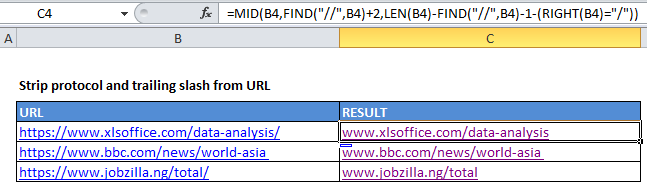
Explanation
In the example shown, the formula in C5 is:
=MID(B4,FIND("//",B4)+2,LEN(B4)-FIND("//",B4)-1-(RIGHT(B4)="/"))
How this formula works
The core of this formula is the MID function, which extracts the text in a URL starting with the character after “//”, and ending with the character before the trailing slash (“/”):
=MID(url,start,chars)
The url comes straight from B4.
The start is calculated using the FIND function like this:
FIND("//",B4)+2
FIND returns the position of the double slash (“//”) in the URL as a number, so we add 2 in order to start extracting at the next character.
Chars represents the number of characters to extract. We calculate this using the following expression:
LEN(B4)-FIND("//",B4)-1-(RIGHT(B4)="/")
The LEN function calculates the length of the original URL, from which we subtract the position of “//” minus 1. we also use a bit of Boolean logic to conditionally subtract 1 more character:
(RIGHT(B4)="/")
Here the RIGHT function extracts the last character which is compared to “/”. A result of TRUE is evaluated as 1, while a result of FALSE is evaluated as 0.
The Boolean logic is used to avoid additional conditional logic.