Normalize text by removing punctuations, extra spaces and more in Excel
To remove some of the natural complexity of text (strip punctuation, normalize case, remove extra spaces) you can use a formula based on the SUBSTITUTE function, with help from the TRIM and LOWER functions.
Instance
There may be times when you need to remove some of the variability of text before other processing.
Case Study
One example is when you want to count specific words inside larger text strings. Because Excel doesn’t provide support for regular expressions, you can’t construct precise matches. For example, if you want to count how many times the word “fox” appears in a cell, you will end up counting “foxes”. You can look for “fox ” (with a space) but that will fail with “fox,” or “fox.” One workaround is to simplify the text first with a formula in a helper column, then run counts on the simplified version. The example on this page shows one way to do this.
Formula
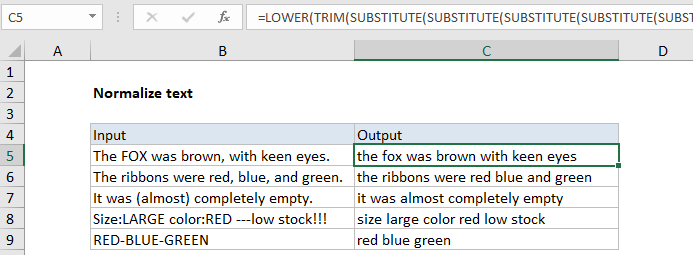
=LOWER(TRIM(SUBSTITUTE(SUBSTITUTE(SUBSTITUTE(SUBSTITUTE(SUBSTITUTE(SUBSTITUTE
(SUBSTITUTE(SUBSTITUTE(A1,"("," "),")"," "),"-"," "),":"," "),";"," "),"!"," "),
","," "),"."," ")))
Explanation
How this formula works
The formula shown in this example uses a series of nested SUBSTITUTE functions to strip out parentheses, hyphens, colons, semi-colons, exclamation marks, commas, and periods. The process runs from the inside out, with each SUBSTITUTE replacing one character with a single space, then handing off to the next SUBSTITUTE. The inner most SUBSTITUTE removes the left parentheses, and the result is handed to the next SUBSTITUTE, which removes the right parentheses, and so on.
In the version below, line breaks have been added for readability, and to make it easier to edit replacements. Excel does not care about line breaks in formulas, so you can use the formula as-is.
=
LOWER(
TRIM(
SUBSTITUTE(
SUBSTITUTE(
SUBSTITUTE(
SUBSTITUTE(
SUBSTITUTE(
SUBSTITUTE(
SUBSTITUTE(
SUBSTITUTE(
A1,
"("," "),
")"," "),
"-"," "),
":"," "),
";"," "),
"!"," "),
","," "),
"."," ")))
After all substitutions are complete, the result is run through TRIM to normalize spaces, then the LOWER function to force all text to lowercase.
Note: You’ll need to adjust the actual replacements to suit your data.
Adding a leading and trailing space
In some cases you may want to add a space character to the start and end of the cleaned text. For example, if you want to count words precisely, you may want to look for the word surrounded by spaces (i.e. search for ” fox “, ” map “) to avoid false matches. To add a leading and trailing space, just concatenate a space (” “) to the start and end:
=" "&formula&" "
Where “formula” is the longer formula above.