How to count specific words in a cell in Excel
If you need to count how many times a specific a word (or any substring) appears inside a cell, you can use a formula that uses SUBSTITUTE and LEN.
Formula
=(LEN(text)-LEN(SUBSTITUTE(text,word,"")))/LEN(word)
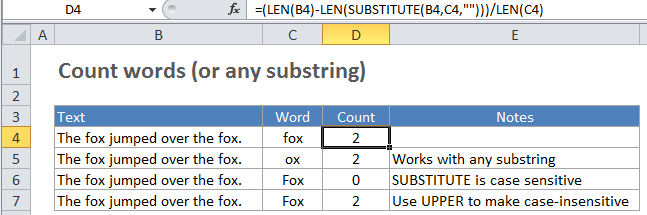
Explanation
In our example, we are using this formula:
=(LEN(B4)-LEN(SUBSTITUTE(B4,C4,"")))/LEN(C4)
How this formula works
B4 is the cell we’re counting words in, and C4 contains the substring (word or any substring) you are counting.
SUBSTITUTE removes the substring from the original text and LEN calculates the length of the text without the substring. This number is then subtracted from the length of the original text. The result is the number of characters that were removed by SUBSTITUTE.
Finally, the number of characters removed is divided by the length of the substring. So, if a substring is 5 characters long, and there are 10 characters missing after it’s been removed from the original text, we know the substring appeared twice in the original text.
Handling problems
Counting words in Excel is tricky because Excel doesn’t support regular expressions. As a result, it’s difficult to build matches that target the words you want to count exactly, while ignoring substrings and other partial matches (look for “fox ” to avoid “foxes”). Punctuation and case variations make this problem quite challenging.
One workaround is to use another formula in a helper column to “normalize text” as a first step. Then use the formula on this page to count words wrapped in space characters to get an accurate count (i.e. you can look for ” fox ” in the normalized text.
Note: this approach is only as good as the normalized text you are able to create, and you might need to adjust the normalizing formula many times to get the result you need.
Handling case
SUBSTITUTE is a case-sensitive function, so it will match case when running a substitution. If you need to count both upper and lower case occurrences of a word or substring, use the UPPER function inside SUBSTITUTE to convert the text to uppercase before running the substitution:
=(LEN(B4)-LEN(SUBSTITUTE(UPPER(B4),UPPER(C4),"")))/LEN(C4)
Because this formula converts the substring and the text to uppercase before performing the substitution, it will work equally well with text in any case.