How to count keywords in a range of cell
To count the number of specific words or keywords that appear in a given cell, you can use a formula based on the SEARCH, ISNUMBER, and SUMPRODUCT functions.
Formula
=SUMPRODUCT(--ISNUMBER(SEARCH(keywords,A1)))
Note: if a keyword appears more than once in a given cell, it will only be counted once. In other words, the formula only counts instances of different keywords.
Explanation
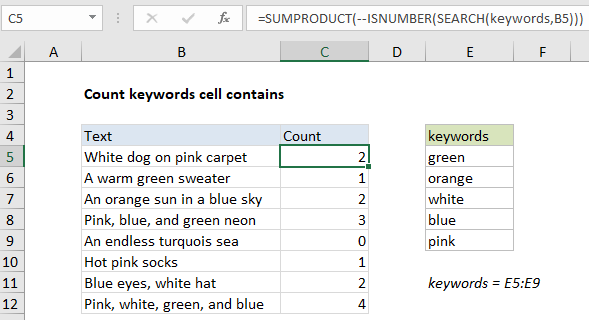
In the example shown, the formula in C5 is:
=SUMPRODUCT(--ISNUMBER(SEARCH(keywords,B5)))
where “keywords” is the named range E5:E9.
How this formula works
The core of this formula is the ISNUMBER + SEARCH approach to finding text in a cell, which is explained in more detail here. In this case, we are looking in each cell for all words in the named range “keywords” (E5:E9). We do this by passing the range into SEARCH as the find_text argument. Because we pass in an array of 5 items:
{"green";"orange";"white";"blue";"pink"}
we get an array of 5 items back as a result:
{#VALUE!;#VALUE!;1;#VALUE!;14}
Numbers correspond to matches, and the #VALUE! error means no match was found. In this case, because we don’t care where the text was found in the cell, we use ISNUMBER to convert the array into TRUE and FALSE values:
{FALSE;FALSE;TRUE;FALSE;TRUE}
And the double negative (–) to change these into 1s and zeros:
{0;0;1;0;1}
The SUMPRODUCT function then simply returns the sum of the array, 2 in this case.
Handling empty keywords
If the keyword range contains empty cells, the formula won’t work correctly, because the SEARCH function returns zero when looking for an empty string (“”). To filter any empty cells in the keyword range, you can use the variation below:
{=SUMPRODUCT(--ISNUMBER(SEARCH(IF(keywords<>"",keywords),B5)))}