FORECAST function: Description, Usage, Syntax, Examples and Explanation
What is FORECAST function in Excel?
Syntax of FORECAST function
FORECAST(x, known_y’s, known_x’s)
The FORECAST function syntax has the following arguments:
- X Required. The data point for which you want to predict a value.
- Known_y’s Required. The dependent array or range of data.
- Known_x’s Required. The independent array or range of data.
FORECAST formula explanation
- If x is nonnumeric, FORECAST returns the #VALUE! error value.
- If known_y’s and known_x’s are empty or contain a different number of data points, FORECAST returns the #N/A error value.
- If the variance of known_x’s equals zero, then FORECAST returns the #DIV/0! error value.
- The equation for FORECAST is a+bx, where:
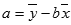 and:
and:
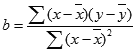
and where x and y are the sample means AVERAGE(known_x’s) and AVERAGE(known y’s).
Example of FORECAST function
Steps to follow:
1. Open a new Excel worksheet.
2. Copy data in the following table below and paste it in cell A1
Note: For formulas to show results, select them, press F2 key on your keyboard and then press Enter.
You can adjust the column widths to see all the data, if need be.
| Known Y | Known X | |
| 6 | 20 | |
| 7 | 28 | |
| 9 | 31 | |
| 15 | 38 | |
| 21 | 40 | |
| Formula | Description | Result |
| =FORECAST(30,A2:A6,B2:B6) | Predicts a value for y given an x value of 30 | 10.607253 |