Calculate periods for annuity in Excel
To calculate the number of periods needed for an annuity to reach a given future value, you can use the NPER function.
Formula
=NPER(rate,pmt,pv,fv,type)
Explanation
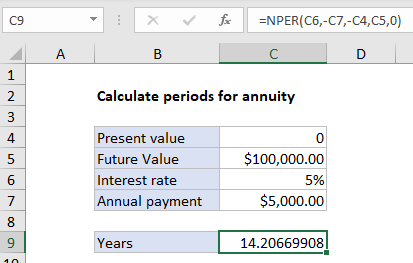
In the example shown C9 contains this formula:
=NPER(C6,-C7,-C4,C5,0)
Explanation
An annuity is a series of equal cash flows, spaced equally in time. The goal in this example is to calculate the years required to save 100,000 by making annual payments of $5,000 where the interest rate is 5% and the starting amount is zero. Payments are made annually, at the end of each year. To solve for periods, the NPER function is configured like this:
- rate – from cell C6, 5%.
- pmt – from C7, $5,000 (entered as negative value)
- pv – from cell C4, 0.
- fv – from cell C5, 100000.
- type – 0, payment at end of period (regular annuity).
With this information, the NPER function returns 14.20669908 years. Note both payment and present value are entered as negative values, since these are cash outflows.