Get last working day in month in Excel
If you need to determine the last working day of a given month and year, then this tutorials is for you.
To get the last working day in a month, you can use the WORKDAY function together with the EOMONTH function. See example below:
Formula
=WORKDAY(EOMONTH(date)+1,-1)
>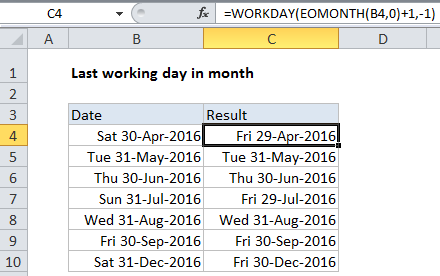
In the example, the formula in C4 is:
=WORKDAY(EOMONTH(B4,0)+1,-1)
Explanation
Working from the inside out, the EOMONTH function gets the last day of month of any date. To this result, we add 1, which results in the first day of the next month.
This date goes into WORKDAY function as the “start date”, along with -1 for “days”. The WORKDAY function automatically steps back 1 day, taking into account any weekends. The result is the last workday of the month.
Holidays
To get the last working day of the month, taking into account holidays, just add the range that contains holiday dates to the formula like this:
=WORKDAY(EOMONTH(B4,0)+1,-1,holidays)
Custom weekends
The WEEKDAY function assumes weekends are Saturday and Sunday. If you need to customize weekend days, you can use the WEEKDAY.INTL function.