Get fiscal year from date in Excel
To get a fiscal year from a date, you can use a formula based on the YEAR and MONTH functions.
Formula
=YEAR(date)+(MONTH(date)>=startmonth)
Explanation
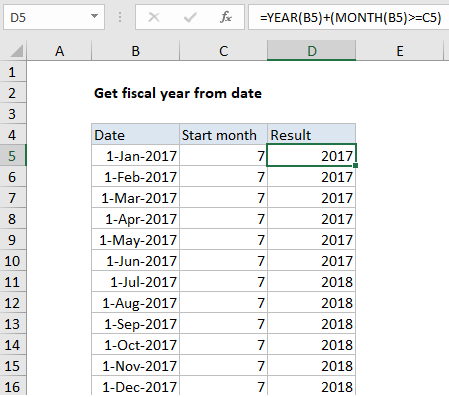
In the example shown, the formula in D5 is:
=YEAR(B5)+(MONTH(B5)>=C5)
How this formula works
By convention a fiscal year is denoted by the year in which it ends. So, if a fiscal year begins in July, then the date August 1, 2018 is in fiscal year 2019.
The year function first returns the year from the date in B5, 2017. To this result, the following boolean expression is added:
(MONTH(B5)>=C5)
Here, the MONTH function returns the month from the date in B5, 1, and this result is compared to the start month in C5. Since 1 is less than 7, the expression returns FALSE, which evaluates to zero.
Note: with boolean logic, TRUE values are evaluated as 1 and FALSE values are evaluated as zero. Therefore, if the month from the date is greater than or equal to the start month, the expression returns TRUE, or 1. If not, the expression returns FALSE, or zero.