Basic Overtime Calculation Formula in Excel
If you need to find basic overtime calculation formula in Excel then this tutorials is for you. See the example below.
To calculate overtime and pay associated with overtime, you can use the formulas explained on this page.
Formula
=(reg_hrs*rate)+(ot_hrs*rate*1.5)
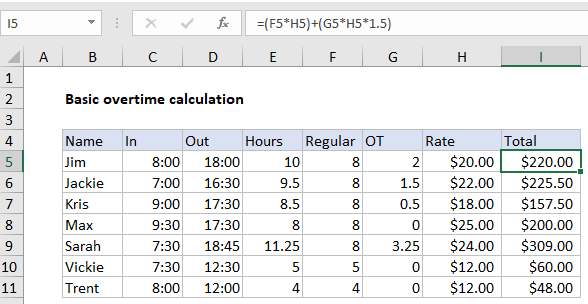
Explanation
In formula in cell I5 is:
=(F5*H5)+(G5*H5*1.5)
How this formula works
Note: it’s important to understand that Excel deals with time natively as fractions of a day. So, 12:00 PM is .5, 6:00 AM is .25, 6 PM is .75, and so on. This works fine for standard time and date calculations, but in many cases you’ll want to convert times to decimal hours to make other calculations more straightforward. In the example shown on this page, we capture time in native units, but then convert to decimal hours in column E.
To calculate total hours worked, cell E5 contains:
=(D5-C5)*24
This is simply end time minus start time, multiplied by 24 to convert to decimal hours.
To calculate regular time, F5 contains:
=MIN(8,E5)
This is an example of using MIN instead of IF to simplify. The result is the smaller of two options: 8 hours, or regular time as calculated above.
To calculate OT (overtime), G5 contains:
=E5-F5
Not much to see here. We simply subtract regular time from total hours to get overtime. Note the result will be zero if total time = regular time. This is important because it effectively “zeroes out” the overtime component of the formula in I5 when there is no overtime.
To calculate the Total, I5 contains:
(F5*H5)+(G5*H5*1.5)
This is where we finally calculate a total based on rate and hours, taking into account overtime paid at 1.5 times the normal rate. (Adjust the multiplier as needed). We first multiply regular time by the normal rate. Then we multiply overtime by the same rate times 1.5. As mentioned above, when overtime is zero, this part of the formula returns zero.
Finally, the sum of both calculations above is returned as the Total in column I.