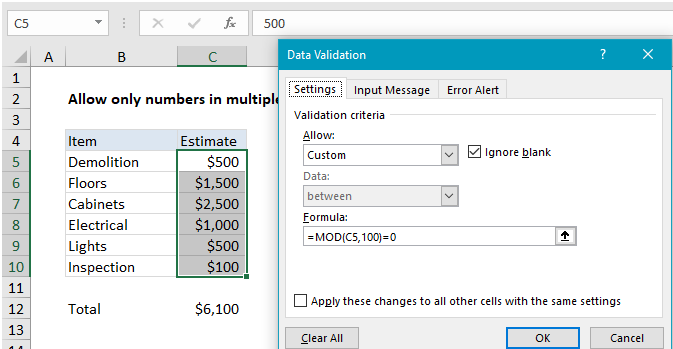
Excel Data validation number multiple 100
Accept only numbers that are multiple of 100
Formula
=MOD(A1,100)=0
Note: Cell references in data validation formulas are relative to the upper left cell in the range selected when the validation rule is defined, in this case C5.
Explanation
In the example shown, the data validation applied to C5:C10 is:
=MOD(C5,100)=0
How this formula works
Data validation rules are triggered when a user adds or changes a cell value. When a custom formula returns TRUE, validation passes and the input is accepted. When the formula returns FALSE, validation fails and the input is rejected.
In this case, the MOD function is used to perform a modulo operation, which returns the remainder after division. The formula used to validate input is:
=MOD(C5,100)=0
The value in C5 is 500. The MOD function divides 500 by 100 and gets 5, with a remainder of zero. Since 0 = 0, The rule returns TRUE and the data validation passes:
=MOD(500,100)=0 =0=0 =TRUE
If a user enters, say, 550, the remainder is 50, and validation fails:
=MOD(C5,100)=0 =MOD(550,100)=0 =50=0 =FALSE