How to test for all values in a range are at least in Excel
To test if all values in a range are at least a certain threshold value, you can use the COUNTIF function together with the NOT function.
Formula
=NOT(COUNTIF(range,"<65"))
Explanation
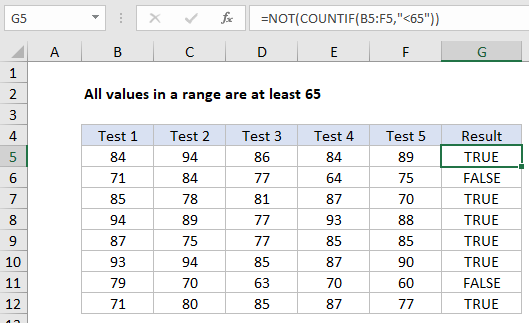
In the example shown, the formula in G5 is:
=NOT(COUNTIF(B5:F5,"<65"))
How this formula works
At the core, this formula uses the COUNTIF function to count any cells that fall below a given value, which is hardcoded as 65 in the formula:
COUNTIF(B5:F5,"<65")
In this part of the formula, COUNTIF will return a positive number if any cell in the range is less than 65, and zero if not. In the range B5:F5, there is one score below 65 so COUNTIF will return 1.
The NOT function is used to convert the number of from COUNTIF into a TRUE or FALSE result. The trick is that NOT also “flips” the result at the same time:
- If any values are less than 65, COUNTIF returns a positive number and NOT returns FALSE
- f no values are less than 65, COUNTIF returns a zero and NOT returns TRUE
This is the equivalent of wrapping COUNTIF inside IF and providing a “reversed” TRUE and FALSE result like this:
=IF(COUNTIF(B5:F5,"<65"),FALSE,TRUE)