Count and Sum Functions in Excel
The most used functions in Excel are the functions that count and sum.
COUNT function is one of the STATISTICAL functions while SUM function is one of the Math and Trig functions.
You can count and sum based on one criteria or multiple criteria.
Count
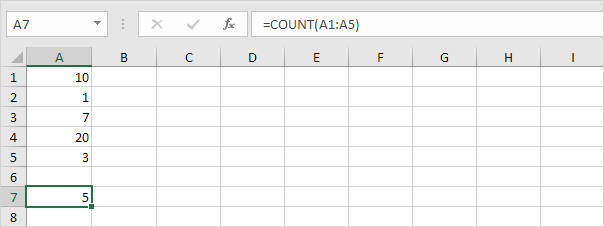
To count the number of cells that contain numbers, use the COUNT function.
Countif
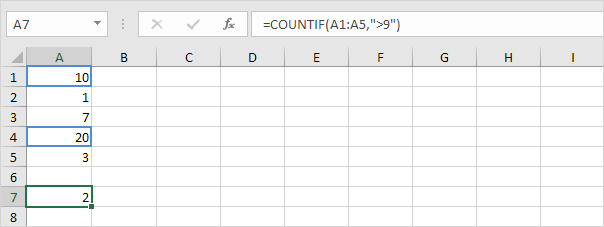
To count cells based on one criteria (for example, greater than 9), use the following COUNTIF function.
Countifs
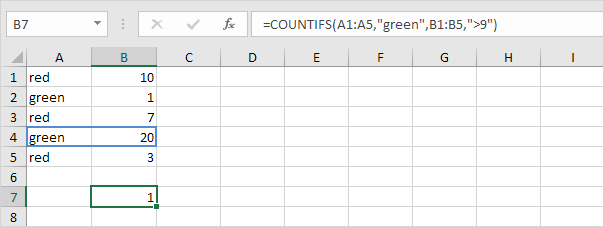
To count cells based on multiple criteria (for example, green and greater than 9), use the following COUNTIFS function.
Sum
To sum a range of cells, use the SUM function.
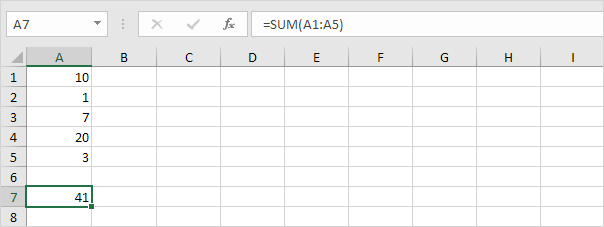
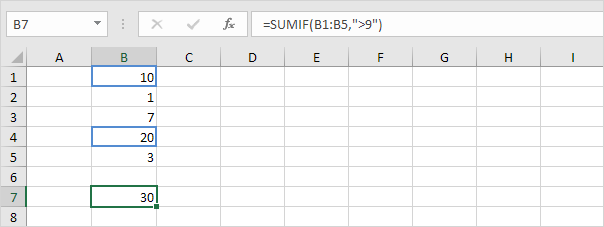
Sumif
To sum cells based on one criteria (for example, greater than 9), use the following SUMIF function (two arguments).
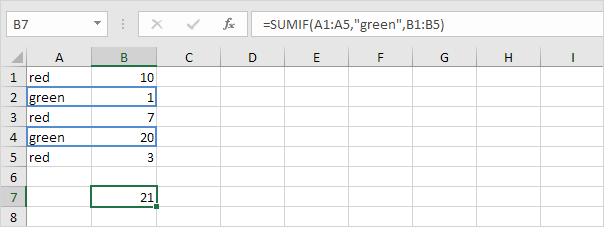
To sum cells based on one criteria (for example, green), use the following SUMIF function (three arguments, last argument is the range to sum).
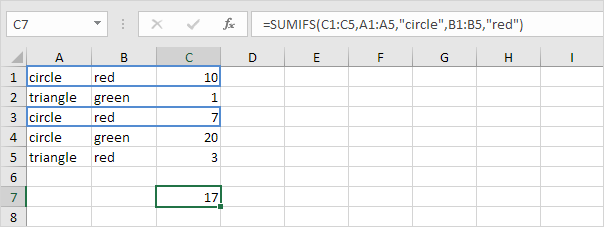
Sumifs
To sum cells based on multiple criteria (for example, circle and red), use the following SUMIFS function (first argument is the range to sum).
General note: in a similar way, you can use the AVERAGEIF and AVERAGEIFS function to average cells based on one or multiple criteria.