If cell is greater than in Excel
This tutorial shows how to calculate If cell is greater than in Excel using the example below;
Formula
=IF(A1>30,"Yes","No")
Explanation
If you want to take an action when a cell value is greater than a certain value, you can use the IF function to test a value and return one value if the test is true, and another if the test is false.
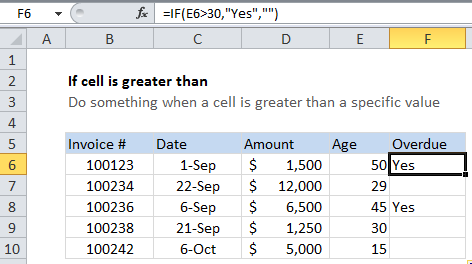
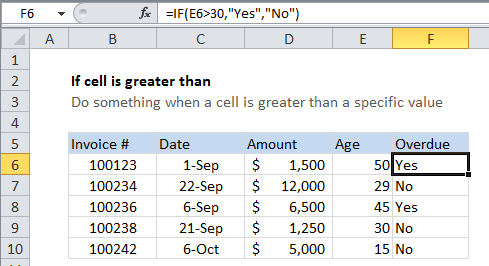
In the example shown, we are using this formula in cell F6.
=IF(E6>30,"Yes","No")
This formula simply tests the value in cell E6 to see if it’s greater than 30. If so, the test returns TRUE, and the IF function returns “Yes” (the value if TRUE).
If the test returns FALSE, the IF function returns “No” (the value if FALSE).
Return nothing if FALSE
You might want to display “Yes” if invoices or overdue and nothing if not. This makes the report cleaner, and easier to read. In that case, simple use an empty string (“”) for the value if false:
=IF(E6>30,"Yes","")