Sum entire column in Excel
This tutorial shows how to Sum entire column in Excel using the example below;
Formula
=SUM(A:A)
Explanation
If you want to sum an entire column without supplying an upper or lower bound, you can use the SUM function with and the specific range syntax for entire column.
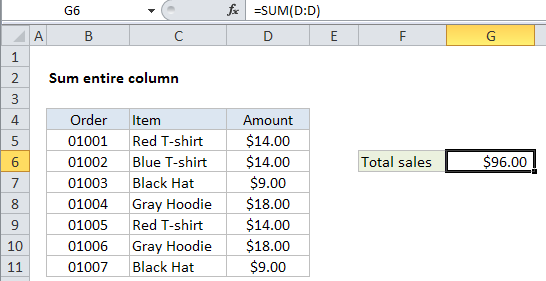
In the example shown, the formula in G6 is:
=SUM(D:D)
How this formula works
Excel supports “full column” and “full row” references like this:
=SUM(A:A) // sum all of column A =SUM(3:3) // sum all of row 3
You can see how this works yourself by typing “A:A”, “3:3”, etc. into the name box (left of the formula bar) and hitting return — Excel will select the entire column or row.
Note: Full column and row references are an easy way to reference data that may change in size, but you need to be sure that you aren’t unintentionally including extra data. For example, if you use =SUM(A:A:) to sum all of column A, and column A also includes a date somewhere (anywhere), this date will be included in the sum.