Sum bottom n values in Excel
This tutorial shows how to Sum bottom n values in Excel. You can use a combination of SUMPRODUCT function and SMALL function to get the sum bottom n values in the example below;
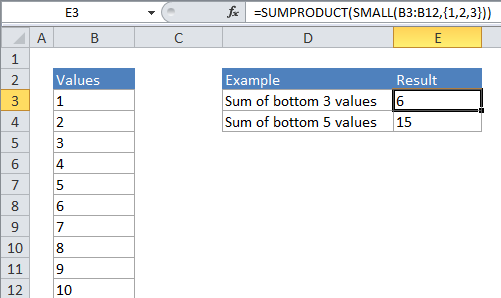
Formula
=SUMPRODUCT(SMALL(range,{1,2,n}))
Explanation
If you need to sum or add the bottom values in a range, you can do so with a formula that uses the SMALL function wrapped inside the SUMPRODUCT function. In the generic form of the formula (above), rng represents a range of cells that contain numeric values and n represents the idea of nth value.
In the example, the active cell contains this formula:
=SUMPRODUCT(SMALL(B4:B13,{1,2,3}))
How this formula works
In its simplest form, SMALL will return the “nth smallest” value in a range. For example, the formula:
=SMALL (A1:A10, 2)
will return the 2nd smallest value in the range A1:A10 which, in the example above, is the number 2.
However, if you supply an “array constant” (e.g. a constant in the form {1,2,3}) to SMALL as the second argument , SMALL will return an array of results instead of a single result. So, the formula:
=SMALL (A1:A10, {1,2,3})
Will return the 1st, 2nd, and 3rd largest value in the range A1:A10. In the example above, where A1:A10 contains the numbers 1-10, the result from SMALL will be the array {1,2,3}. SUMPRODUCT then sums the numbers in this array and returns a total, which is 6.
Using SUMPRODUCT avoids the complexity of entering an array formula, but it is still processing arrays. You can also write an array formula directly using SUM like so:
{=SUM(SMALL(B4:B13,{1,2,3}))}
Note that you must enter this formula as an array formula.
Large N
When N becomes large it becomes tedious to create the array constant by hand – if you want to sum to the bottom 20 or 30 values in a big list of values, typing out an array constant with 20 or 30 items will take a long time. In this case, you can use a shortcut for building the array constant that uses the ROW and INDIRECT functions. For example, if you want to SUM the bottom 20 values in a range called “rng” you can write a formula like this:
=SUMPRODUCT(SMALL(rng,ROW(INDIRECT("1:25"))))
Variable N in another cell
To set up the a formula where N is a variable in another cell, you can concatenate inside INDIRECT. For example, if A1 contains N, you can use:
=SUMPRODUCT(SMALL(range,ROW(INDIRECT("1:"&A1))))
This allows a user to change the value of N directly on the worksheet.