Lookup value between two numbers in Excel
This tutorial shows how to Lookup value between two numbers in Excel using the example below;
Formula
=LOOKUP(B5,minimums,results)
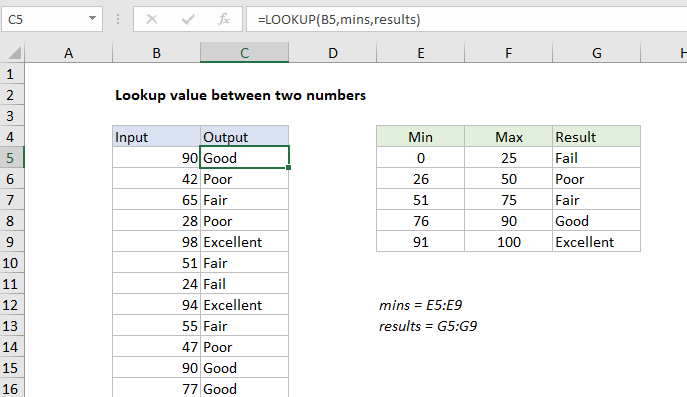 Explanation
Explanation
To lookup values between two values and return a corresponding result, you can use the LOOKUP function and a sorted table. In the example shown, the formula in C5 is:
=LOOKUP(B5,mins,results)
where “mins” is the named range E5:E9, and “results” is the named range G5:G9.
How this formula works
The LOOKUP function does an approximate match lookup in one range, and returns the corresponding value in another.
Although the table in this example includes both maximum and minimum values, we only need to use the minimum values. This is because when LOOKUP can’t find a match, it will match the next smallest value. LOOKUP is configured like this:
- The lookup values come from column B.
- The lookup vector is entered as the named range “mins” (E5:E9)
- The result vector is entered as the named range “results” (G5:G9)
LOOKUP behaves like this:
- If LOOKUP encounters an exact match in the lookup vector, the corresponding value in the result vector is returned.
- If no exact match is found, LOOKUP will traverse the lookup vector until a larger value is found, then “step back” to the previous row and return a result.
- If the lookup value is greater than the largest value in the lookup vector, LOOKUP will return a result associated with the last value in the lookup vector.
Note: values in the lookup vector must be sorted in ascending order.
Literally between
Although the example above works fine, and effectively locates a value “between” a min and max in the lookup table, it really only uses the min values. With a named range “maxs” for maximum values, you can write a literal version of the formula like this:
=LOOKUP(2,1/((B5>=mins)*(B5<=maxs)),results)
This version returns the associated value in the result vector when the value in B5 is literally between both the min and max value in a given row. In case of duplicates, this formula will return the last match.