Lookup latest price in Excel
This tutorial shows how to Lookup latest price in Excel using the example below;
Formula
=LOOKUP(2,1/(item="hat"),price)
Explanation
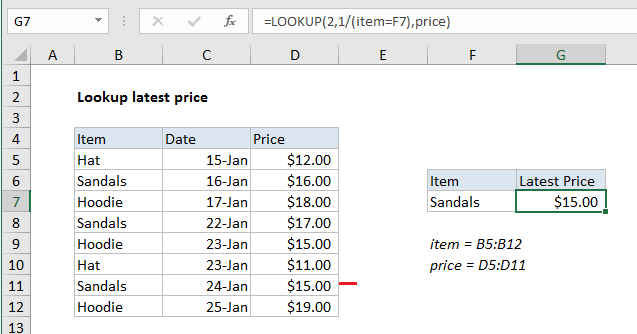
To lookup the most recent price for an item in a list, where latest items appear last, you can use a formula based on the LOOKUP function. In the example show, the formula in G7 is:
=LOOKUP(2,1/(item=F7),price)
where item is the named range B5:B12, and price is the named range D5:D11.
How this formula works
The LOOKUP function assumes data is sorted, and always does an approximate match. If the lookup value is greater than all values in the lookup array, default behavior is to “fall back” to the last previous value. This formula exploits this behavior by creating an array that contains only 1s and errors, then deliberately looking for the value 2, which will never be found.
LOOKUP searches the array for a value of 2, falls back to the last 1, and returns a value at the corresponding position in the results array.
First, this expression is evaluated:
item=F7
When F7 contains “sandals” the result is:
{FALSE;TRUE;FALSE;TRUE;FALSE;FALSE;TRUE;FALSE}
which next serves as the divisor to 1, producing the final lookup array:
{#DIV/0!;1;#DIV/0!;1;#DIV/0!;#DIV/0!;1;#DIV/0!}
The lookup function looks for 2, then falls back to the last 1 (position 7 in the array), and returns the 7th item on the lookup array, a price of $15.