Split numbers from units of measure in Excel
To split a number from a unit value, you need to determine the position of the last number. If you add 1 to that position, you have the start of the unit text.
Note: these is an experimental formula that uses a hard coded array constant, set down here for reference and comment. Casually tested only, so take care if you use or adapt.
Sometimes you encounter data that mixes units directly with numbers (i.e. 8km, 12v, 7.5hrs). Unfortunately, numbers in this format are considered to be text inside of Excel, and you won’t be able to perform any math operations on such values.
Formula
=MAX(ISNUMBER(VALUE(MID(A1,{1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9},1)))*{1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9})+1
Explanation
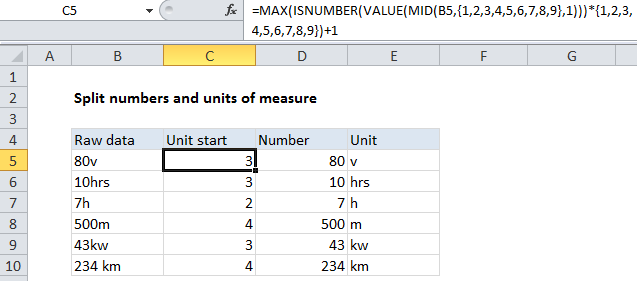
In the example shown, the formula in C5 is:
=MAX(ISNUMBER(VALUE(MID(B5,{1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9},1)))*{1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9})+1
This formula uses the MID function to extract the first 9 values in B5, one character at a time. The result is an array like this:
{“8″,”0″,”v”,””,””,””,””,””,””}
We then use the VALUE function to convert numbers in text format to actual numbers. The result is:
{8,0,#VALUE!,#VALUE!,#VALUE!,#VALUE!,#VALUE!,#VALUE!,#VALUE!}
We run this array through ISNUMBER to get:
{TRUE,TRUE,FALSE,FALSE,FALSE,FALSE,FALSE,FALSE,FALSE}
Then multiply that times another array with 9 numbers to get:
{1,2,0,0,0,0,0,0,0}
Then we use MAX to get the largest value, which is the position of the “last number”.
In this case we add 1 to the position to get the “unit start” position.
Finally, we use this position with standard LEFT and RIGHT functions to separate the numbers from the units:
=VALUE(LEFT(B5,C5-1)) // number =TRIM(RIGHT(B5,LEN(B5)-C5+1)) // unit
Note that the hard-coded number array constant is a hack for convenience, and will only handle raw values up to 9 characters in length.