Join first and last name — Manipulating NAMES in Excel
If you need to join separate first and last names together into a single full name, you can easily do so with concatenation using the ampersand (&) character. In the formula below, first is first name, and last is last name.
Formula
=first&" "&last
Explanation
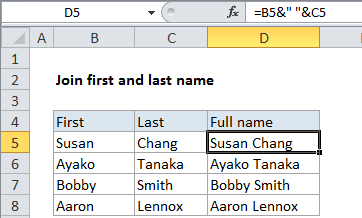
In the example, the active cell contains this formula:
=B4&" "&C4
How this formula works
The ampersand character (&) is a special operator in Excel that is used for concatenation. Concatenation is just a fancy word for “join”.
On the formula, the text in B4 “Susan” is being joined to a space character ” ” and then to the text in cell C4, “Chang”.
Whenever you use concatenation with literal text entered directly inside the formula, make sure to enclose the text in double quotes (“”). The ampersands are never enclosed in quotes unless you want an ampersand to appear in the result of a formula as literal text.
With CONCATENATE
You can also use the CONCATENATE function to join text. For this example, the formula would be:
=CONCATENATE(B4," ",C4)
The CONCATENATE function keeps things tidy, but the ampersand creates shorter, more flexible formulas.