How to extract last two words from text string in Excel
To extract the last two words from a cell, you can use a formula built with several Excel functions, including MID, FIND, SUBSTITUTE, and LEN.
Formula
=MID(A1,FIND("@",SUBSTITUTE(A1," ","@",LEN(A1)-LEN(SUBSTITUTE(A1," ",""))-1))+1,100)
Explanation
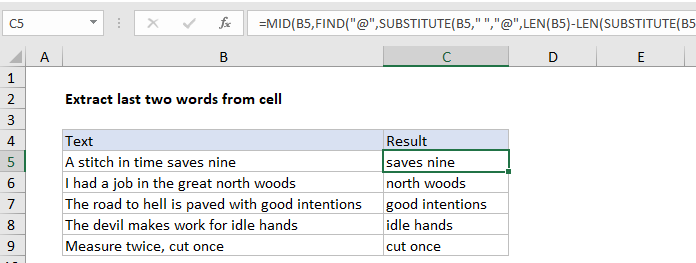
In the example shown, the formula in C5 is:
=MID(B5,FIND("@",SUBSTITUTE(B5," ","@",LEN(B5)-LEN(SUBSTITUTE(B5," ",""))-1))+1,100)
How this formula works
At the core, this formula uses the MID function to extract characters starting at the second to last space. The MID function takes 3 arguments: the text to work with, the starting position, and the number of characters to extract.
The text comes from column B, and the number of characters can be any large number that will ensure the last two words are extracted. The challenge is to determine the starting position, which is just after the second to last space. The clever work is done primarily with the SUBSTITUTE function, which has an optional argument called instance number. This feature is used to replace the second to last space in the text with the “@” character, which is then located with the FIND function.
Working from the inside out, the snippet below figures out how many spaces are in the text total, from which 1 is subtracted.
LEN(B5)-LEN(SUBSTITUTE(B5," ",""))-1
In the example shown, there are 5 spaces in the text, so the code above returns 4. This number is fed into the outer SUBSTITUTE function as instance number:
SUBSTITUTE(B5," ","@",4)
This causes SUBSTITUTE to replace the forth space character with “@”. The choice of @ is arbitrary. You can use any character that will not appear in the original text.
Next, the FIND locates the “@” character in the text:
FIND("@","A stitch in time@saves nine")
The result of FIND is 17, to which 1 is added to get 18. This is the starting position, and goes into the MID function as the second argument. For simplicity, the number of characters to extract is hardcoded as 100. This number is arbitrary and can be adjusted to fit the situation.
Extract last N words from cell
This formula can be generalized to extract the last N words from a cell by replacing the hardcoded 1 in the example with (N-1). In addition, if you are extracting many words, you may want to replace the hardcoded argument in MID, 100, with a larger number. To guarantee you the number is large enough, you could simply use the LEN function as follows:
=MID(B5,FIND("@",SUBSTITUTE(B5," ","@",LEN(B5)-LEN(SUBSTITUTE(B5," ",""))-(N-1)))+1,LEN(B5))