How to check if cell contains number in Excel
To test if a cell (or any text string) contains a number, you can use the FIND function together with the COUNT function. In the generic form of the formula (above), A1 represents the cell you are testing. The numbers to be checked (numbers between 0-9) are supplied as an array.
Formula
=COUNT(FIND({0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9},A1))>0
Explanation
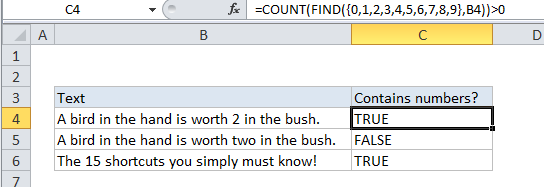
In the example the formula in C4 is:
=COUNT(FIND({0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9},B4))>0
How this formula works
The FIND function returns the position of the text when it’s found in the cell, and the #VALUE! error if not. In the example, the cell B4 contains the number “2” in the 29th position. So, if we just used this formula:
=FIND("2",B4)
It would return the number 29 as the result. However, because we are giving the FIND function an array of items to check, it will return an array of results that looks like this:
{#VALUE!,#VALUE!,29,#VALUE!,#VALUE!,#VALUE!,#VALUE!,#VALUE!,#VALUE!,#VALUE!}
In other words, FIND checks the contents of B4 for each number and returns the result of each check as an item in the array.
After FIND returns the array, COUNT counts the items in the array. COUNT only counts numeric values, so any #VALUE! item in the array is treated as zero. COUNT will return a number greater than zero if there are any numbers in the array, and zero if not.
The last step in the formula is to compare the result the FIND and COUNT functions with zero. If there were any numbers found, the formula will return TRUE. If not, the formula will return FALSE.
If you want to do something more than just test whether a cell contains text, you can wrap the formula in an IF statement like so:
=IF(COUNT(FIND({0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9},B4))>0, "Yes", "No")
Instead of returning TRUE or FALSE, the formula above returns “Yes” if B4 contains any numbers and “No” if not.
Cell equals number?
If you only need to test if a cell equals a number, you can use the ISNUMBER function like this:
=ISNUMBER(A1)