Round by bundle size in Excel
This tutorials shows how to Round by bundle size in Excel.
To round up to the next bundle size, you can use the CEILING function which automatically rounds up away from zero.
To round up to the next bundle size, you can use the CEILING function which automatically rounds up away from zero.
Formula
=CEILING(number,bundle)/bundle
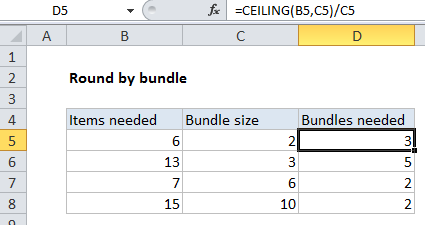
Explanation
In the example shown, we need a certain number of items, and the items come in specific bundle sizes. To calculate how many items are needed, taking into account the bundle size, the formula in D5 is:
=CEILING(B5,C5)/C5
How this formula works
The gist of this formula is that it figures out bundles needed, given items needed, and a specific bundle size.
For example, if you need 6 items, and the bundle size is 2, you’ll need 3 bundles. If you need 3 items, and the bundle size is 5, you’ll need 1 bundle (and you’ll end up with 2 extra items).
First, we use the CEILING function get an item count needed, taking into account the bundle size.
=CEILING(B5,C5)
The CEILING function is fully automatic. It will round a number up until it reaches a number evenly divisible by a given multiple (bundle in this case).
Finally, we divide the number provided by CEILING by the original bundle size.
The result is the the total number of bundles required.