Calculate loan interest in given year in Excel
To calculate the total interest for a loan in a given year, you can use the CUMIPMT function.
Formula
=CUMIPMT(rate,nper,pv,start,end,type)
Explanation
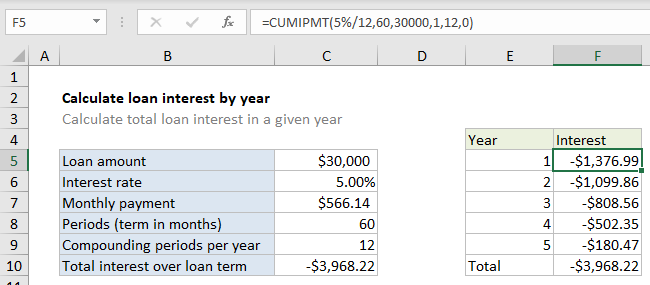
In the example shown, the total interest paid in year 1 is calculated by using 1 for start period and 12 for end period. The The formula in F5 is:
=CUMIPMT(5%/12,60,30000,1,12,0)
Note: values hardcoded for readability only.
How this formula works
For this example, we want to calculate the interest paid during each year in a 5-year loan of $30,000 with an interest rate of 5%. To do this, we set up CUMIPMT like this:
- start_period – the starting period for a given year.
- end_period – the ending period for a given year.
- rate – The interest rate per period. We divide 5% by 12 because 5% represents annual interest.
- nper – the total number of payment periods for the loan, 60.
- pv – The present value, or total value of all payments now, 30000.
In the range F5:F9, here are the formulas used:
=CUMIPMT(5%/12,60,30000,1,12,0) // year 1 =CUMIPMT(5%/12,60,30000,13,24,0) // year 2 =CUMIPMT(5%/12,60,30000,25,36,0) // year 3 =CUMIPMT(5%/12,60,30000,37,48,0) // year 4 =CUMIPMT(5%/12,60,30000,49,60,0) // year 5
Note many values could be picked up directly with cell references, but are hardcoded in this example for readability.
Other periods
In this example, we are calculating interest by year, so periods are set up accordingly. However, you can adjust periods to calculate interest in any time frame desired.