Next biweekly payday from date in Excel
To get the next payday – assuming a biweekly schedule, with paydays on Friday – you can use a formula based on the CEILING function.
Formula
=CEILING(date+1,14)-1
Explanation
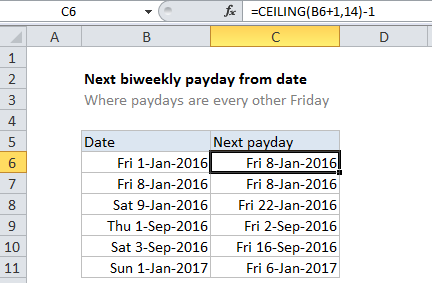
In the example shown, the formula in C6 is:
=CEILING(B6+1,14)-1
Note: this formula assumes Excel’s default 1900 date system.
How this formula works
This formula depends on the CEILING function, which rounds numbers up to a given multiple. It works because how dates work in Excel’s default 1900 date system, where the first day in the system is the number 1, equal to the date Sunday January 1, 1900.
In this scheme, the first Friday is day number 6, the second Friday is day number 13, and day 14 is the second Saturday. What this means is that all second Saturday’s in the future are evenly divisible by 14.
The formula uses this fact to figure out 2nd Saturdays, then subtracts 1 to get the Friday previous.
The other every other Friday
If you need to get the alternate Friday in an every other Friday scheme, you can use this version of the formula:
=CEILING(A1+8,14)-8
The idea is the same, but the formula needs to roll forward 8 days to get to an even multiple of 14. Once CEILING returns a date, 8 days are subtracted to move back to the Friday previous.