Calculate expiration date in Excel
If you need to calculate an expiration in the future, you can use a variety of formulas.
See example below;
Formula
=A1+30 // 30 days
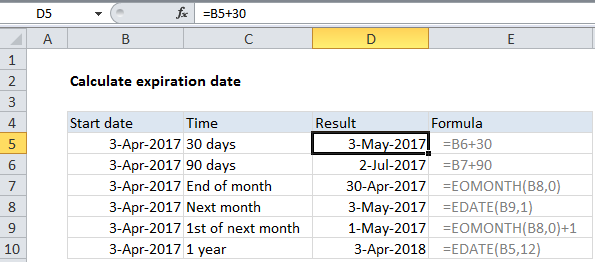
Explanation
In the example shown, the formulas used in column D are:
=B5+30 // 30 days =B5+90 // 90 days =EOMONTH(B7,0) // end of month =EDATE(B8,1) // next month =EOMONTH(B7,0)+1 // 1st of next month =EDATE(B10,12) // 1 year
Important
In Excel, dates are simply serial numbers. In the standard date system for windows, based on the year 1900, where January 1, 1900 is the number 1. This means that January 1, 2050 is the serial number 54,789.
- If you are calculating a date n days in the future, you can add days directly as in the first two formulas.
- An easy way to calculate the 1st day of a month is to use EOMONTH to get the last day of the previous month, then simply add 1 day.
- If you need an expiration date at the end month, use the EOMONTH function, which returns the last day of the month, n months in the future or past.
- If you want to count by months, you can use the EDATE function, which returns the same date n months in the future or past.