Excel Data validation exists in list
Using the example below, this tutorial shows how to create Data validation exists in list in Excel.
Formula
=COUNTIF(list,A1)>0
 Explanation
Explanation
Note: Excel has a built-in data validation rules for dropdown lists. This page explains how to create a your own validation rule for lists when you don’t want the dropdown behavior.
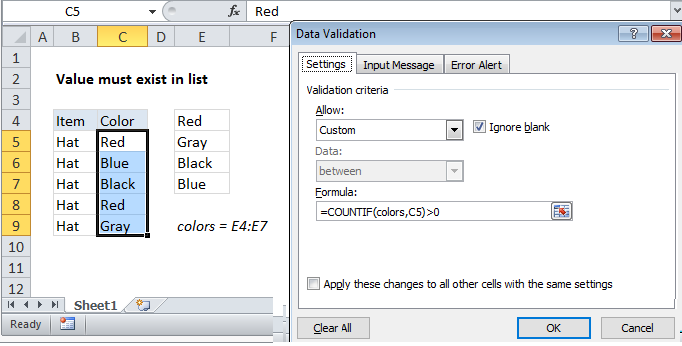
To allow only values from a list in a cell, you can use data validation with a custom formula based on the COUNTIF function.
In the example shown, the data validation applied to C5:C9 is:
=COUNTIF(colors,C5)>0
How this formula works
Data validation rules are triggered when a user adds or changes a cell value.
In this case, the COUNTIF function is part of an expression that returns TRUE when a value exists in a specified range or list, and FALSE if not.
The COUNTIF function simply counts occurrences of the value in the list. Any count greater than zero will pass validation.
Note: Cell references in data validation formulas are relative to the upper left cell in the range selected when the validation rule is defined, in this case C5.