How to count specific characters in a cell in Excel
To count how many times a specific character appears in a cell, you can use a formula based on the SUBSTITUTE and LEN functions.
Formula
=LEN(A1)-LEN(SUBSTITUTE(A1,"a",""))
Explanation
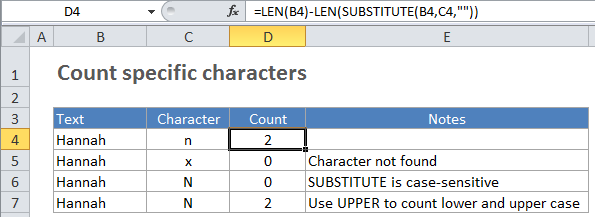
In the example, the active cell contains this formula:
=LEN(B3)-LEN(SUBSTITUTE(B3,C3,""))
How this formula works
This formula works by using SUBSTITUTE to first remove all of the characters being counted in the source text. Then the length of the text (with the character removed) is subtracted from the length of the original text. The result is the number of characters that were removed with SUBSTITUTE, which is equal to the count of those characters.
Upper and lower case
SUBSTITUTE is a case sensitive function, so it will match case when running a substitution. If you need to count both upper and lower case occurrences of a specific character, use the UPPER function inside SUBSTITUTE to convert the text to uppercase before running the substitution. Then supply an uppercase character as the text that’s being substituted like this:
=LEN(A1)-LEN(SUBSTITUTE(UPPER(A1),"A",""))