COUNTIF with non-contiguous range in Excel
This tutorial shows how to COUNTIF with non-contiguous range in Excel using the example below;
Formula
=SUM(COUNTIF(INDIRECT({"range1","range2","range3"}),criteria))
Explanation
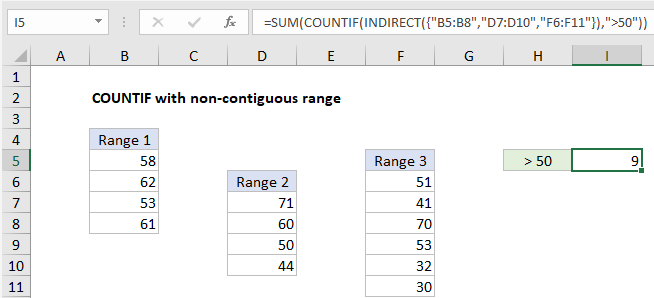
To use count a non-contiguous range with criteria, you can use the COUNTIF function together with INDIRECT and SUM. In the example shown, cell I5 contains this formula:
=SUM(COUNTIF(INDIRECT({"B5:B8","D7:D10","F6:F11"}),">50"))
How this formula works
COUNTIF counts the number of cells in a range that meet given criteria. If you try to use COUNTIF with multiple ranges separated by commas, you’ll get an error. One solution is to write out the ranges as text in an array constant inside the INDIRECT function like this:
INDIRECT({"B5:B8","D7:D10","F6:F11"})
INDIRECT will evaluate the text values and pass the multiple ranges into COUNTIF. Because COUNTIF receives more than one range, it will return more than one result in an array. We use the SUM function to “catch” and handle the array:
=SUM({4,2,3})
The SUM function then returns the sum of all values, 9. Although this is an array formula, it does not require CSE, since we are using an array constant.
Note: INDIRECT is a volatile function and can impact workbook performance.
Multiple COUNTIFs
Another way to solve this problem is to use more than one COUNTIF:
=COUNTIF(B5:B8,">50")+COUNTIF(D7:D10,">50")+COUNTIF(F6:F11,">50")
With a limited number of ranges, this approach may be easier to implement. It avoids possible performance impacts of INDIRECT, and allows a normal formula syntax for ranges, so ranges will update automatically with worksheet changes.
Single cell ranges
With single cell ranges, you can write a formula without COUNTIF like this:
=(A1>50)+(C1>50)+(E1>50)
Each expression returns TRUE or FALSE, when are coerced to 1 and zero during the math operation. This is an example of using boolean logic in a formula.