If else in Excel
This tutorial shows how to calculate If else in Excel using the example below;
Formula
=IF(test, true result, false result)
Explanation
If you need to test a condition, then take one action if the condition is TRUE, and another action if the condition if FALSE, you can use the IF function.
Context
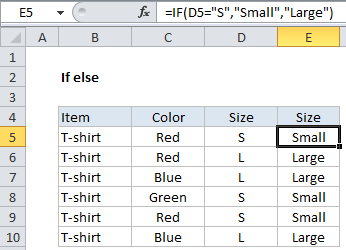
In the example shown, we have a list of T-shirts that includes color and size. However, the size is abbreviated as “S” for small and “L” for large. Lets say you want to write a formula to expand these abbreviations and show either the word “Small” or “Large” in column E. In other words:
- If a cell in column D contains “S”, return “Small”.
- If a cell in column D contains “L”, return “Large”.
This is a perfect application of the IF function.
Solution
The IF function is organized like this:
=IF(test, true result, false result)
In the example, we need to test cells in column D to see what they contain, so the formula we are using in cell E5 is:
=IF(D5="S","Small","Large")
Translated, this says:
IF cell D5 equals (contains) the letter “S”, return the word “Small”, ELSE return the word “Large”.
Notice we are only testing for “S” — we don’t need to test for “L”. That’s because we only have two possible values, and the ELSE part of the formula (the FALSE result) logically takes care of “L” for us: if the cell doesn’t contain “S”, it must be “L”.
Nesting IFs to handle more conditions
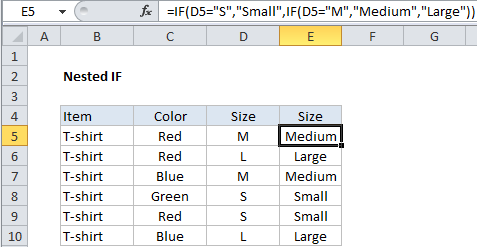
This works fine for two conditions, but what if we have a third condition?, for example, “M” for “Medium”?
In that case, we need to extend the formula with another IF statement. We put the second IF statement, replacing the false result.
In the example below, we’ve added another size (Medium). The formula we are using in E5 is:
=IF(D5="S","Small",IF(D5="M","Medium","Large"))
This technique is called “nesting”, since we are placing on function inside another. With it is used with the IF function, you’ll sometimes hear it called a “Nested IF statement”.