Print Excel Sheet In Landscape Or Portrait
Excel can fit three more columns of information on the page in landscape mode than it can in portrait mode. By default, paper orientation is mostly portrait. This article shows how to change paper orientation in Excel before printing a worksheet or workbook.
Print a worksheet in landscape or portrait orientation
Steps to change page orientation in Excel
Because many worksheets are wider than they are tall (such as budgets or sales tables that track expenditures over a period of time), you may find the need to switch the orientation from the default portrait mode to landscape mode.
a. Page Layout tab → Page Setup group → Orientation button reveals a drop-down menu with these two options:
- Portrait
- Landscape
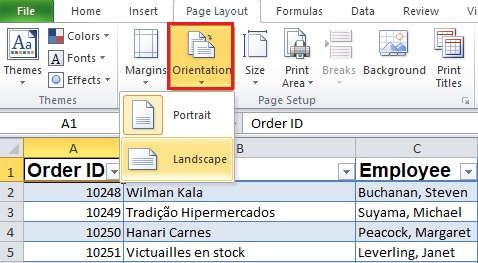
For report, portrait orientation may work better.
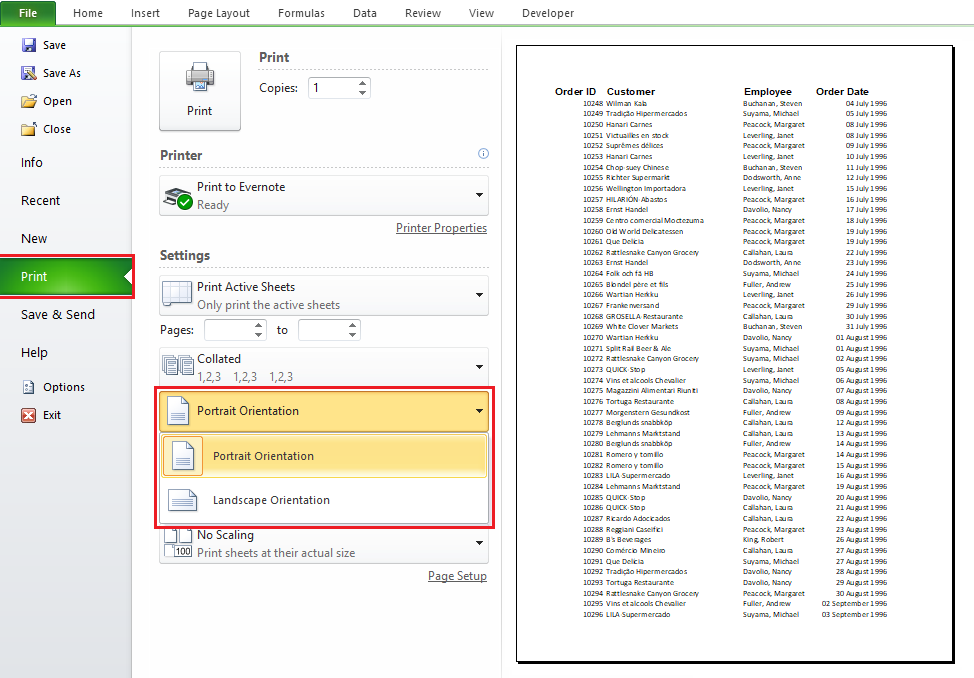
b. Change the page orientation when you are ready to print
-
Select the worksheet, worksheets, or worksheet data that you want to print.
- Click File > Print.
- In the Page Orientation drop-down box, under Settings, click Portrait Orientation or Landscape Orientation.
- When you are ready to print, click Print.