Create dynamic workbook reference to another workbook in Excel
To build a dynamic worksheet reference – a reference to another workbook that is created with a formula based on variables that may change – you can use a formula based on the INDIRECT function. See example below:
Formula
=INDIRECT("'["&workbook&"]"&sheet&"'!"&ref)
Explanation
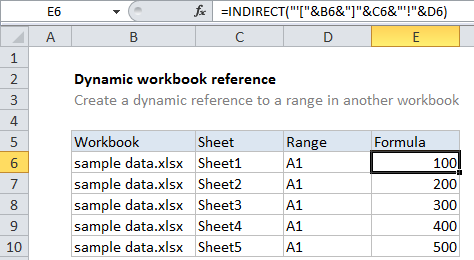
In the example shown, the formula in E6 is:
=INDIRECT("'["&B6&"]"&C6&"'!"&D6)
How this formula works
The gist of this formula is to build up a complete reference to a range in another workbook as text, then use the INDIRECT function to convert the text to an actual reference.
A reference to an external worksheet looks like this:
‘[sample data.xlsx]Sheet1’!A1
Note the square brackets ([ ]) around workbook name, single quotes (‘ ‘) around the worksheet + sheet, and the exclamation mark (!) that follows.
To create a reference like this using text, we use concatenation to join values from columns B, C, and D with the required brackets, quotes, and exclamation mark:
=INDIRECT("'["&B6&"]"&C6&"'!"&D6)
The result is fed into INDIRECT as the ref_text:
=INDIRECT("'[sample data.xlsx]Sheet1'!A1")
The INDIRECT function then evaluates the text and converts it to a reference. Excel follows the reference and returns the value at the given reference.
Note: if the reference is invalid, or if the workbook referenced is not open, INDIRECT will throw a #REF error. You can catch this error with the IFERROR function and display a custom result if you like.