Count dates in given year in Excel
This tutorial shows how to Count dates in given year in Excel using the example below;
Formula
=SUMPRODUCT(--(YEAR(dates)=year))
Explanation
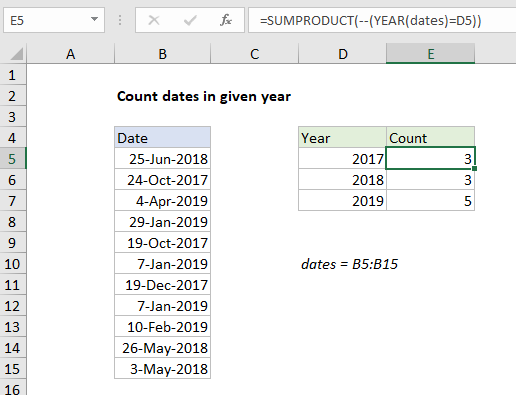
To count dates in a given year, you can use the SUMPRODUCT and YEAR functions. In the example shown, the formula in E5 is:
=SUMPRODUCT(--(YEAR(dates)=D5))
where “dates” the a named range B5:B15.
How this formula works
The YEAR function extracts the year from a valid date. In this case, we are giving YEAR and array of dates in the named range “dates”, so we get back an array of results:
{2018;2017;2019;2019;2017;2019;2017;2019;2019;2018;2018}
Each date is compared to the year value in column D, to produce an array or TRUE FALSE values:
{FALSE;TRUE;FALSE;FALSE;TRUE;FALSE;TRUE;FALSE;FALSE;FALSE;FALSE}
For the formula in E5, TRUE values are cases where dates are in the year 2017, and FALSE values represent dates in any other year.
Next, we use a double negative to coerce the TRUE FALSE values to 1’s and 0’s. Inside SUMPRODUCT, we now have:
=SUMPRODUCT({0;1;0;0;1;0;1;0;0;0;0})
Finally, with only one array to work with, SUMPRODUCT sums the items in the array and returns a result, 3.