Get position of 2nd 3rd and more instance of character in Excel
To get the position of the 2nd, 3rd, 4th, etc. instance of a specific character inside a text string, you can use the FIND and SUBSTITUTE functions.
Note: we use “~” in this case only because it rarely occurs in other text. You can use any character that you know won’t appear in the text.
Formula
=FIND("~",SUBSTITUTE(text,char,"~",instance))
Explanation
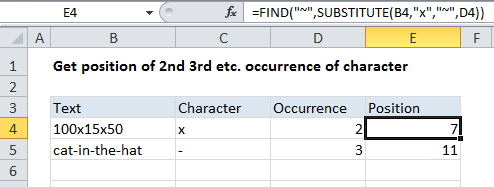
In the example shown, the formula in E4 is:
=FIND("~",SUBSTITUTE(B4,"x","~",D4))
How this formula works
At the core, this formula uses the fact that the SUBSTITUTE function understands “instance”, supplied as an optional forth argument called “instance_num”. This means you can use the SUBSTITUTE function to replace a specific instance of a character in a text string. So:
SUBSTITUTE(B4,"x","~",D4)
replaces only the 2nd instance (2 comes from D4) of “x” in text in B4, with “~” character. The result looks like this:
100×15~50
Next, FIND locates the “~” inside this string and returns the position, which is 7 in this case.