Convert Excel time to Unix time in Excel
This tutorial shows how to Convert Excel time to Unix time in Excel using example below.
To convert a time in Excel’s format to a Unix time stamp, you can use a formula based on the DATE function.
Formula
=(A1-DATE(1970,1,1))*86400
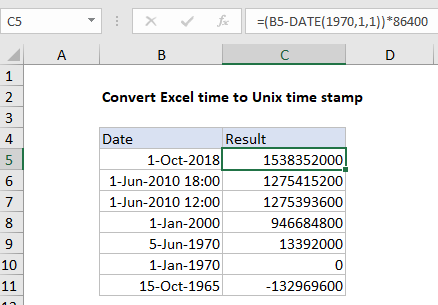
>
Explanation
In the example shown, the formula in C5 is:
=(B5-DATE(1970,1,1))*86400
How this formula works
The Unix time stamp tracks time as a running count of seconds. The count begins at the “Unix Epoch” on January 1st, 1970, so a Unix time stamp is simply the total seconds between any given date and the Unix Epoch. Since a day contains 86400 seconds (24 hours x 60 minutes x 60 seconds), conversion to Excel time can be done by subtracting the date value for the Unix Epoch and multiplying days by 86400.
In the example shown, the formula first subtracts the date value for January 1, 1970 from the date value in B5 to get the number of days between the dates, then multiplies the result by 85400 to convert to a Unix time stamp. The formula evaluates like this:
=(B5-DATE(1970,1,1))*86400 =(43374-25569)*86400 =1538352000
How Excel tracks dates time
The Excel date system starts on January 1, 1900 and counts forward. The table below shows the numeric values associated with a few random dates:
| Date | Raw value |
|---|---|
| 1-Jan-1900 | 1 |
| 28-Jul-1914 00:00 | 5323 |
| 1-Jan-1970 00:00 | 25569 |
| 31-Dec-1999 | 36525 |
| 1-Oct-2018 | 43374 |
| 1-Oct-2018 12:00 PM | 43374.5 |
Notice the last date includes a time as well. Since one day equals 1, and one day equals 24 hours, time in Excel can represented as fractional values of 1, as shown in the table below. In order to see the value displayed as a time, a time format needs to be applied.
| Hours | Time | Fraction | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 3:00 AM | 3/24 | 0.125 |
| 6 | 6:00 AM | 6/24 | 0.25 |
| 4 | 4:00 AM | 4/24 | 0.167 |
| 8 | 8:00 AM | 8/24 | 0.333 |
| 12 | 12:00 PM | 12/24 | 0.5 |
| 18 | 6:00 PM | 18/24 | 0.75 |
| 21 | 9:00 PM | 21/24 | 0.875 |
| 24 | 12:00 AM | 24/24 | 1 |