How to sum a total in multiple Excel tables
To sum a total in multiple tables, you can use the SUM function and structured references to refer to the columns to sum. See example below:
Formula
=SUM(Table1[column],Table2[column])
Note: the total row must be enabled. If you disable a total row, the formula will return the #REF error.
Explanation
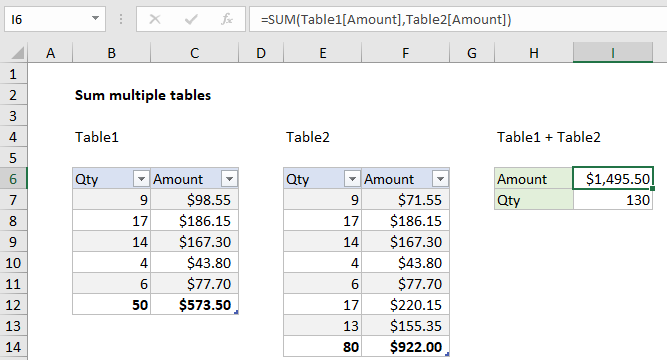
In the example shown, the formula in I6 is:
=SUM(Table1[Amount],Table2[Amount])
How this formula works
This formula uses structured references to refer to the “Amount” column in each table. The structured references in this formula resolve to normal references like this:
=SUM(Table1[Amount],Table2[Amount]) =SUM(C7:C11,F7:F13) =1495.5
When rows or columns are added or removed from either table, the formula will continue to return correct results. In addition, the formula will work even if the tables are located on different sheets in a workbook.
Alternative syntax with Total row
It is also possible to reference the total row in a table directly, as long as tables have the Total Row enabled. The syntax looks like this:
Table1[[#Totals],[Amount]]
Translated: “The value for Amount in the Total row of Table1”.
Using this syntax, the original formula above could be re-written like this:
=SUM(Table1[[#Totals],[Amount]],Table2[[#Totals],[Amount]])
As above, this formula will work even when the table is moved or resized.