Cash denomination calculator in Excel
To calculate required currency denominations, given a specific amount, you can build a currency calculation table as shown in the example. This solution uses the INT and SUMPRODUCT functions.
Formula
=INT((amount-SUMPRODUCT(denoms,counts))/currentdenom)
Explanation
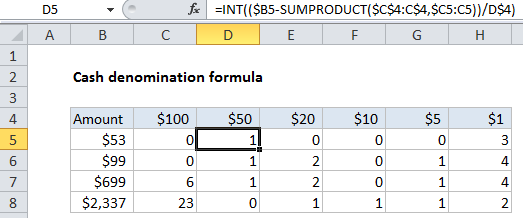
In the example show, the formula in D5 is:
=INT(($B5-SUMPRODUCT($C$4:C$4,$C5:C5))/D$4)
How this formula works
To start off, the formula in C5 is:
=INT($B5/C$4)
This formula divides the amount in column B by the denomination in C4 (100) and discards the remainder using the INT function. The formulas in column C are simpler than those in the next several columns because this is the first denomination – we don’t need to worry about previous counts.
Next in D5 we first figure out what the value of existing denomination counts with:
SUMPRODUCT($C$4:C$4,$C5:C5)
Here SUMPRODUCT is configured with two arrays, both configured carefully.
Array1 consists of denominations from row 4. This range is carefully constructed to be “expand” when copied across the table to the right. The first reference is absolute ($C$4) and the second reference is “mixed” (C$4) – the row is locked but the column will change, causing the range to expand.
Array2 consists of existing denomination counts from row 5, with the same approach as above. The range will expand as it’s copied to the right.
The result of this SUMPRODUCT operation is the total value of existing denomination counts so far in the table. This is subtracted from the original value in column B, then divided by the “current” denomination from row 4. As before, we use INT to remove any remainder.
As the formulas in column C are copied across the table, the correct counts for each denomination are calculated.
Checking the result
If you want to check your results, add a column to the end of the table with a formula like this:
=SUMPRODUCT(C$4:H$4,C5:H5)
In each row, SUMPRODUCT multiplies all counts by all denominations and returns a result that should match the original values in column B.