How to check worksheet name exists in Excel
To test if a worksheet name exists in a workbook, you can use a formula based on the ISREF and INDIRECT functions.
Formula
=ISREF(INDIRECT("sheetname"&"!A1"))
Explanation
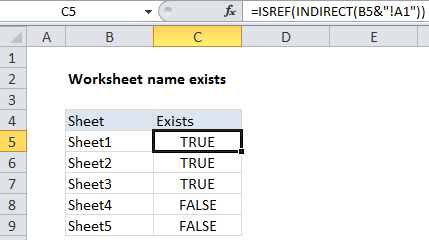
In the example shown, the formula in C5 is:
=ISREF(INDIRECT(B5&"!A1"))
How this formula works
The ISREF function returns TRUE for a valid worksheet reference and FALSE is not.
In this case, we want to find out of a particular sheet exists in a workbook, so we construct a full reference by concatenating the sheet names in column B with an exclamation mark and “A1”:
B5&"!A1"
This returns the text:
"Sheet1!A1"
which goes into the INDIRECT function. INDIRECT then tries to evaluate the text as a reference.
When INDIRECT succeeds, the reference is passed into ISREF which returns TRUE. When INDIRECT can’t create a reference, it throws a #REF error, and ISREF returns FALSE.
Dealing with spaces and punctuation in sheet names
If sheet names contain spaces, or punctuation characters, you’ll need to adjust the formula to wrap the sheet name in single quotes like this:
=ISREF(INDIRECT("'"&sheetname&"'!A1"))