IF with boolean logic in Excel
This tutorial shows how to calculate IF with boolean logic in Excel using the example below;
Formula
= IF(criteria1*criteria2*criteria3,result)
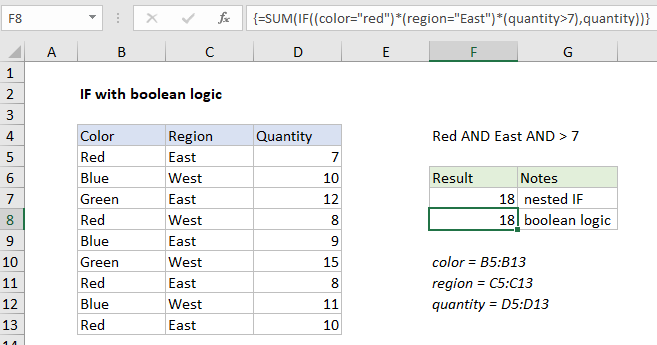
Explanation
In the example shown, the formula in F8 is:
{=SUM(IF((color="red")*(region="East")*(quantity>7),quantity))}
Note: this is an array formula, and must be entered with control + shift + enter.
How this formula works
Note: This example demonstrates how to replace a nested IF formula with a single IF in an array formula using boolean logic. This technique can be used to reduce complexity in complex formulas. However, the example is for illustration only. This particular problem could be easily solved with SUMIFS or SUMPRODUCT.
The formulas in F7 and F8 return the same result, but have different approaches. In cell F7, we have the following formula, using a nested IF approach:
{=SUM(IF(color="red",IF(region="east",IF(quantity>7,quantity))))}
This is how Excel evaluates the IFs inside SUM:
=IF({TRUE;FALSE;FALSE;TRUE;FALSE;FALSE;TRUE;FALSE;TRUE},
IF({TRUE;FALSE;TRUE;FALSE;TRUE;FALSE;TRUE;FALSE;TRUE},
IF({FALSE;TRUE;TRUE;TRUE;TRUE;TRUE;TRUE;TRUE;TRUE},quantity)))
In essence, each IF “filters” values into the next IF, and only quantities where all three logical tests return TRUE “survive” the operation. Other quantities become FALSE and are evaluated by SUM as zero. The final result inside SUM is an array of values like this:
=SUM({FALSE;FALSE;FALSE;FALSE;FALSE;FALSE;8;FALSE;10})
FALSE values evaluate to zero, and the SUM function returns a final result of 18.
In F8 we have this formula, which uses a single IF and boolean logic:
=SUM(IF((color="red")*(region="East")*(quantity>7),quantity))
Each logical expression returns a an array of TRUE and FALSE values. When these arrays are multiplied together, the math operation coerces values to ones and zeros in a single array like this:
IF({0;0;0;0;0;0;1;0;1},quantity)
The array of 1s and 0s filters out irrelevant data, and the same result delivered to SUM:
=SUM({FALSE;FALSE;FALSE;FALSE;FALSE;FALSE;8;FALSE;10})
As before, SUM returns a final result of 18.