How to use Excel MATCH Function
This Excel tutorial explains how to use the MATCH function with syntax and examples.
Excel MATCH function Description
MATCH is an Excel function used to locate the position of a lookup value in a row, column, or table. MATCH supports approximate and exact matching, and wildcards (* ?) for partial matches. Often, the INDEX function is combined with MATCH to retrieve the value at the position returned by MATCH.
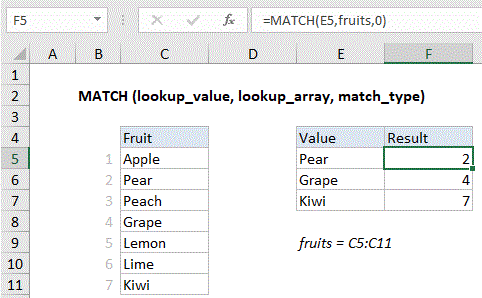
Basic exact match example
Explanation: When match type is set to zero, MATCH performs an exact match. In the example above; the formula in E3 is: MATCH(E2,B3:B11,0)
Return
Syntax
Arguments
- lookup_value – The value to match in lookup_array.
- lookup_array – A range of cells or an array reference.
- match_type – [optional] How to match, specified as -1, 0, or 1. Default is 1.
Note: Match type information
- If match_type is 1, MATCH finds the largest value that is less than or equal to lookup_value. The lookup_array must be sorted in ascending order.
- If match_type is 0, MATCH finds the first value exactly equal to lookup_value. lookup_array does not need to be sorted.
- If match_type is -1, MATCH finds the smallest value that is greater than or equal to lookup_value. The lookup_array must be sorted in descending order.
- If match_type is omitted, it is assumed to be 1.
- Note: All match types will find an exact match.
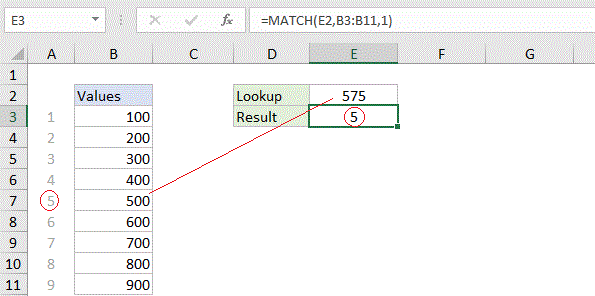
Basic approximate match
Explanation: When match type is set to 1, MATCH will perform an approximate match on values sorted A-Z, finding the largest value less than or equal to the lookup value. In the example shown below, the formula in E3 is:
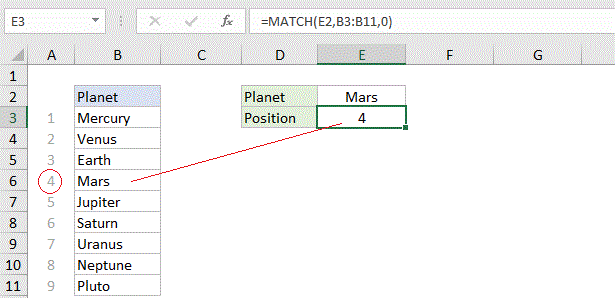
Basic wildcard match

Explanation: When match type is set to zero, MATCH can perform a match using wildcards. In the example shown below, the formula in E3 is: MATCH(E2,B3:B11,0)
This is equivalent to:
MATCH("pq*",B3:B11,0)