How to use Excel GETPIVOTDATA Function
This Excel tutorial explains how to use the GETPIVOTDATA function with syntax and examples.
Excel GETPIVOTDATA function Description
The GETPIVOTDATA function can be used to query an existing pivot table and retrieve specific data based on the pivot table structure. The first argument (data_field) names a value field to query. The second argument (pivot table) is a reference to any cell in an existing pivot table.
Additional arguments are supplied in field/item pairs that act like filters to limit the data retrieved based on the structure of the pivot table. For example, you might supply the field “Region” with the item “East” to limit sales data to sales in the East region.
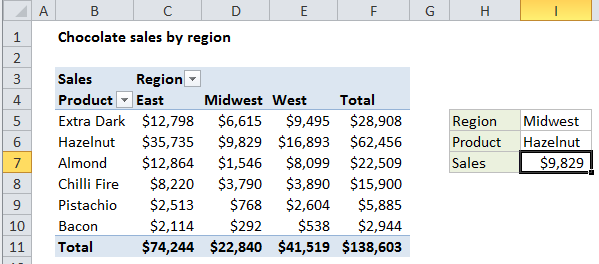
Explanation: The Excel GETPIVOTDATA function can query a pivot table and retrieve specific data based on the pivot table structure, instead of cell references.
Syntax
Arguments
- data_field – The name of the value field to query.
- pivot_table – A reference to any cell in the pivot table to query.
- field1, item1 – [optional] A field/item pair.