Sum if one criteria multiple columns in Excel
This tutorial shows how to Sum if one criteria multiple columns in Excel using the example below;
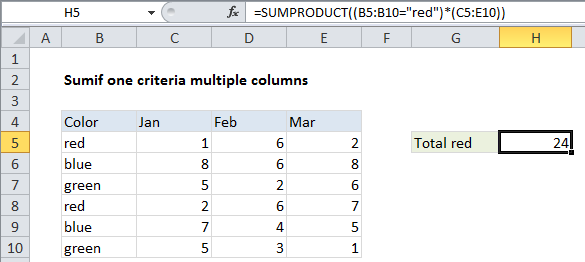
Formula
=SUMPRODUCT((criteria_range="red")*(sum_range))
Explanation
To sum multiple columns conditionally, using one criteria, you can use a formula based on the SUMPRODUCT function. In the example show, the formula in H5 is:
=SUMPRODUCT((B5:B10="red")*(C5:E10))
How this formula works
This first expression in SUMPRODUCT is the criteria, checking if cells in B5:B10 contain “red”. The result is an array of TRUE FALSE values like this:
{TRUE;FALSE;FALSE;TRUE;FALSE;FALSE}
This is multiplied by the values in range C5:E10:
{1,6,2;8,6,8;5,2,6;2,6,7;7,4,5;5,3,1}
The result inside SUMPRODUCT is:
=SUMPRODUCT({1,6,2;0,0,0;0,0,0;2,6,7;0,0,0;0,0,0})
which returns 24, the sum of all values in C5:E10 where B5:B10=”red”.
Contains type search
SUMPRODUCT doesn’t support wildcards, so if you want to do a “cell contains specific text” type search, you’ll need to use criteria that will return TRUE for partial matches. One option is to use the ISNUMBER and SEARCH functions like this:
=SUMPRODUCT((ISNUMBER(SEARCH("red",B5:B10)))*(C5:E10)).